Saturated Fat And Heart Disease
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Unhealthy saturated and trans fats. Replacing saturated fat with linoleic acid appears to be beneficial based on the Hooper Cochrane meta-analysis of interventions although other analyses with fewer studies have shown no effect.
 Replacement Of Saturated Fat With Other Types Of Fat Or Carbohydrates Download Scientific Diagram
Replacement Of Saturated Fat With Other Types Of Fat Or Carbohydrates Download Scientific Diagram
Emerging evidence suggests that saturated fats might affect your health differently depending on the food source of the saturated fat.

Saturated fat and heart disease. Replacement of saturated fat by polyunsaturated fat lowers both plasma. The American Heart Association AHA recently published a meta-analysis that confirmed their 60-year-old recommendation to limit saturated fat SFA saturated fatty acid and replace it with polyunsaturated fat to reduce the risk of heart disease based on the strength of 4 Core Trials. To cause atherosclerosis in several animal species especially nonhuman primates 5.
Different substitutions for saturated fat have different effects on risk of coronary heart disease CHD and need to be discussed separately. Delay the build-up of plaque a fatty substance in your arteries. All-cause mortality cardiovascular mortality fatal MIs myocardial infarctions non-fatal MIs stroke coronary heart disease mortality coronary heart disease events.
Replacing saturated fats with polyunsaturated fats decrease cholesterol levels The only 2 double-blind randomized trials in history failed to show that a low-saturated fat diet decreases heart disease 3 meta-analyses published in the past 3 years concluded no decrease in heart disease a ssociated with low saturated fat diet. A new review of published evidence challenges current guidelines that suggest in order to reduce heart disease risk people should generally restrict intake. One meta-analysis of 21 studies said that there was not enough evidence to conclude that saturated fat increases the risk of heart disease but that replacing saturated fat with polyunsaturated fat may indeed reduce risk of heart disease.
Major dietary sources of saturated fatty acids in the United States are full-fat dairy products and red meat 1. 1 And in 1961 the American Heart Association AHA recommended replacing saturated fatty acids SFAs with unsaturated fatty acids UFAs to prevent CVD. LDL cholesterol is a risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
1 However the study offers a unique twist by teasing. Saturated fat in the diet is associated with an increased risk of heart disease. A lower intake of saturated fat implies an increased intake of some other source of calories to maintain caloric balance.
The American Heart Association recommends aiming for a dietary pattern that achieves 5 to 6 of calories from saturated fat. In contrast a recent study from the Netherlands reported a 17 lower risk of ischaemic heart disease for each 5 increase in energy from SFA13 In this study replacement of 5 of energy from SFA with carbohydrate not necessarily whole grain high glycaemic index carbohydrate cis monounsaturated fatty acids polyunsaturated fatty acids or animal protein was associated with 27-37 higher risk of ischaemic heart disease. Saturated fat regardless of type linked with increased heart disease risk.
A handful of recent reports have muddied the link between saturated fat and heart disease. A study published in the November issue of the British Medical Journal revealed findings that at first glance are not that surprising. Eating foods that contain saturated fats raises the level of cholesterol in your blood.
1 The 1980s and 1990s saw a low-fat campaign emerge. Saturated fat can raise bad LDL cholesterol. The 2015 Dietary Guidelines for Americans DGA recommend consuming.
2 International food and nutrient guidelines tend to. The one significant finding was an effect for saturated fats on cardiovascular events. The study found no statistically significant effects of reducing saturated fat on the following outcomes.
Only PUFA replacement of saturated fat lowers CHD events and CVD and total mortality. To clear the atherosclerosis in animals 6 when it is reduced in the diet. And likewise to reverse atherosclerosis in humans.
To assess the evidence for this recommendation meta-analyses. The scientific rationale for decreasing saturated fat in the diet has been and remains based on well-established effects of saturated fat to raise low-density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol a leading cause of atherosclerosis 4. Despite these recommendations heart disease rates which have been linked to saturated fat intake have steadily risen as have obesity and related diseases such as type 2 diabetes which.
78 In addition reducing saturated fat. Unhealthy saturated and trans fats can heighten your risk of heart disease by increasing the bad LDL cholesterol and lowering the good HDL cholesterol. Study results from the 1940s and 1950s suggest that the type and amount of fat play a major role in serum cholesterol levels.
Saturated fat intake has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease CVD and this effect is thought to be mediated primarily by increased concentrations of LDL cholesterol. High levels of LDL cholesterol in your blood increase your risk of heart disease and stroke.
Limit Saturated Fat Is No Longer Evidence Based Advice
 Dietary Villains Part I Fat Phobia It Is
Dietary Villains Part I Fat Phobia It Is
 How Is Heart Disease Risk Affected When Saturated Fat Is Replaced By Other Nutrients The Nutrition Source Harvard T H Chan School Of Public Health
How Is Heart Disease Risk Affected When Saturated Fat Is Replaced By Other Nutrients The Nutrition Source Harvard T H Chan School Of Public Health
 Dietary Fat Intake And The Risk Of Coronary Heart Disease In Women Nejm
Dietary Fat Intake And The Risk Of Coronary Heart Disease In Women Nejm
 1st Review Paper Effects On Coronary Heart Disease Of Increasing Polyunsaturated Fat In Place Of Saturated Fat Biochemstyles
1st Review Paper Effects On Coronary Heart Disease Of Increasing Polyunsaturated Fat In Place Of Saturated Fat Biochemstyles
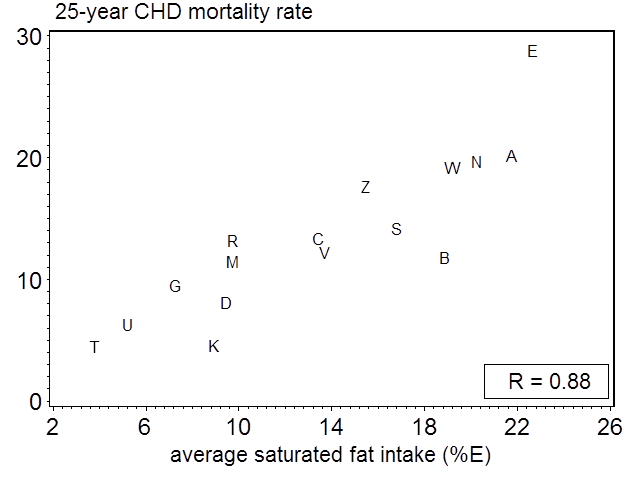 Average Saturated Fat Intake And 25 Year Coronary Heart Disease Rates In The 16 Cohorts Seven Countries Study The First Study To Relate Diet With Cardiovascular Disease
Average Saturated Fat Intake And 25 Year Coronary Heart Disease Rates In The 16 Cohorts Seven Countries Study The First Study To Relate Diet With Cardiovascular Disease
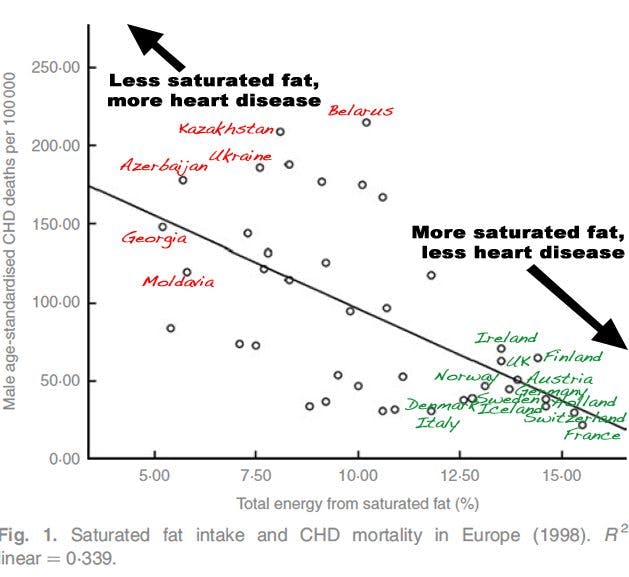 Stunning Saturated Fat And The European Paradox Diet Doctor
Stunning Saturated Fat And The European Paradox Diet Doctor
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/697517-article-saturated-fats-and-unsaturated-fats0230389b-3f6e-4352-95e9-6bb1f3e168f93-59efb531054ad90010e4d96e.png) The Difference Between Saturated And Unsaturated Fats
The Difference Between Saturated And Unsaturated Fats
 Should You Avoid Saturated Fats If You Already Have Heart Disease Advanced Mediterranean Diet
Should You Avoid Saturated Fats If You Already Have Heart Disease Advanced Mediterranean Diet
 Saturated Fat Does Not Clog The Arteries Coronary Heart Disease Is A Chronic Inflammatory Condition The Risk Of Which Can Be Effectively Reduced From Healthy Lifestyle Interventions British Journal Of Sports
Saturated Fat Does Not Clog The Arteries Coronary Heart Disease Is A Chronic Inflammatory Condition The Risk Of Which Can Be Effectively Reduced From Healthy Lifestyle Interventions British Journal Of Sports
 Whole Health Source Does Dietary Saturated Fat Increase Blood Cholesterol An Informal Review Of Observational Studies
Whole Health Source Does Dietary Saturated Fat Increase Blood Cholesterol An Informal Review Of Observational Studies
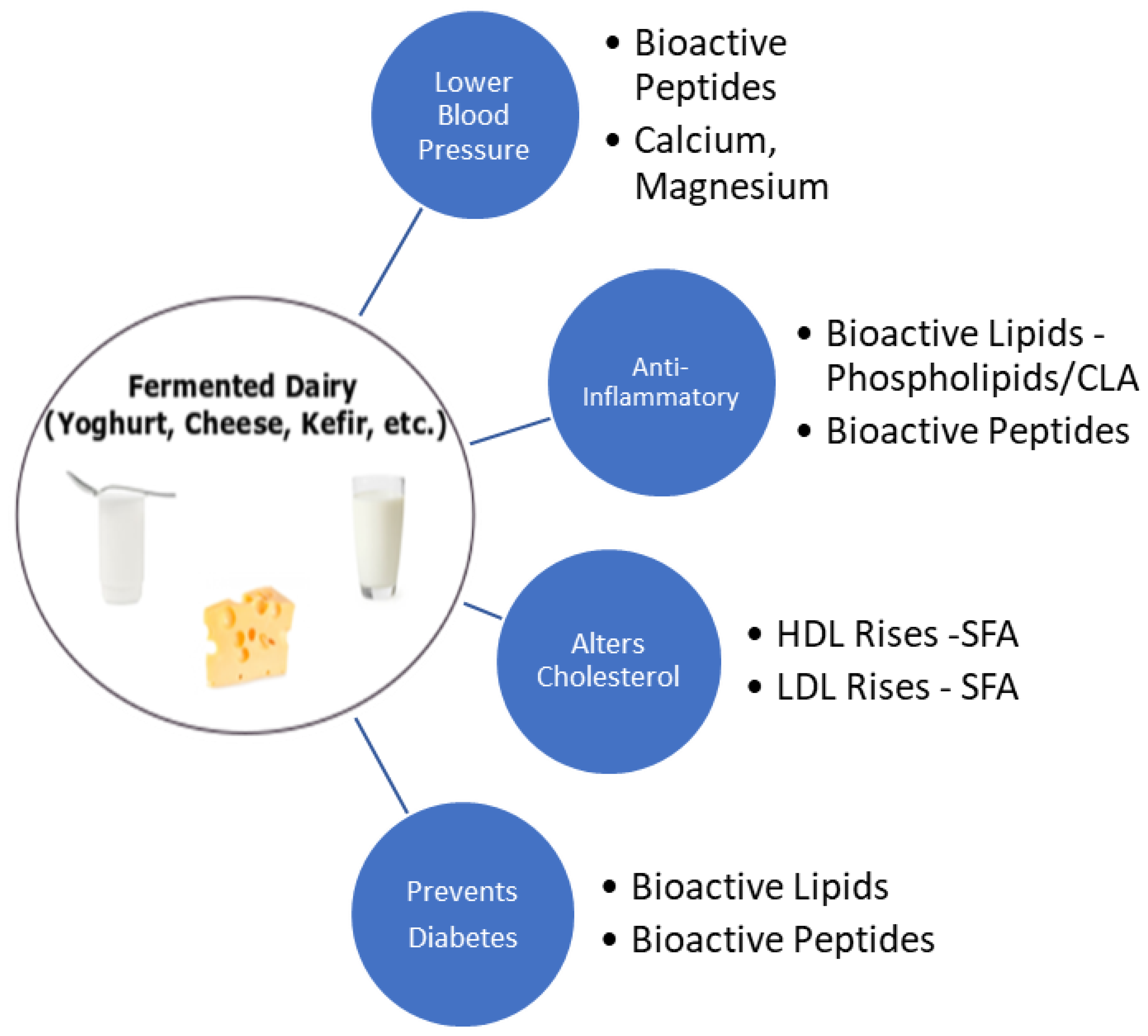 Foods Free Full Text Dairy Fats And Cardiovascular Disease Do We Really Need To Be Concerned Html
Foods Free Full Text Dairy Fats And Cardiovascular Disease Do We Really Need To Be Concerned Html
 What We Know About Saturated Fat And Heart Disease Nutrition Action
What We Know About Saturated Fat And Heart Disease Nutrition Action
 Saturated Fat And Heart Disease Hormonal Obesity Xxxvii The Fasting Method
Saturated Fat And Heart Disease Hormonal Obesity Xxxvii The Fasting Method
Comments
Post a Comment